Together with the awakening of nature, those who we are not happy to see are awakened - ticks. It is in April, as well as in September-October, that the peak of activity of these insects dangerous to humans is observed.
Interestingly, the mites are practically devoid of sight, can smell the scent of the approaching living creature from a distance of 10 meters. They are much more (about 10-15 times) on the roadside than in the forest more often, where there are fewer targets for attack. The life of the mite is 30-50 days.
The main way of getting a tick on a person is when the latter engages a branch, a blade of grass, on which the mite, which was prepared for attack, sits. You can also advise to avoid dry, dead branches - dead mites are loved more than living trees, and in a mixed forest, mites prefer deciduous trees. When passing the route, it should be borne in mind that mites prefer wet shaded places with a thick undergrowth and a grass stand. Even more of them along the paths, roads and in places where cattle graze.
Danger of ticks
The danger of "picking up" a tick is waiting for us not only in nature. To bring an insect into the house can be a dog or a cat that walks along the street, it can be in a bouquet of wildflowers. Also ticks live on mice and rats, inhabiting even the most civilized cities. Ticks carry diseases such as tick-borne encephalitis, tick-borne typhus, tick-borne borreliosis (Lyme disease), hemorrhagic fever, etc.
The tick is especially dangerous because it is very difficult to notice because of the microscopic size of a hungry insect, such a tick is no larger than a poppy seed. The mite itself is a tiny creature of a brownish-brown hue, and the larva is hardly visible to the naked eye at all. Adhering to the human body, the young larva is saturated in about two days, the adult is the same, can remain on the body for up to 12 days and grow to the size of a ball 2 cm in diameter.
The mite never gets drunk at once, from half an hour to several hours, he chooses the place of the bite.This gives a good chance to quickly disarm it. With a very minimal skill, the creeping tick, which touches the hairs on the body, is felt instantly and it can not be confused with anything. The simplest way out - hourly self-and mutual checks, with special attention to the armpits, groin, inner thighs, neck - usually ticks there and bite, and even arriving at a favorite place for a long time trying on and for quite a long time is actually the process of vpivaniya. Comb your hair - the mites often cling to them or crawl into the hair.
It is clear that the possibility for inspections is not always, so you should take care of the appropriate clothing in advance. It can be a trousers tucked into a trouser or a tight shirt, it's better if it's a special suit made of bologna or encephalitis. Under the shirt is good to put tight-fitting body t-shirt or vest, the best option, as described below in the recipe. The jacket is filled in trousers and pulled by a belt. Socks are put on top of the leotard or whatever you have under your trousers. The head and neck are protected with a hood. It's best to walk on the grass in rubber boots - it's hard to get hold of the rubber. Clothes without any cuts and cuts, with tight cuffs on the wrists, ankles, neck. Although it is sometimes possible to find a mite crawling under the tightest cuff, so there are no guarantees. Well, it's certainly dressing up to the maximum for the taiga.
When a tick hits a person's clothing, it begins to move in search of a place for suction, especially mites like axillary cavities, inguinal folds, neck, ears and scalp. If the mite was not seen immediately, then the discomfort begins to disturb only after about 1-2 days, and they manifest themselves in the form of a pulling light pain that arises from the onset of the inflammatory process at the site of the bite. The wound itself, which remains after the tick bite, itches and can not heal for a long time.
What to do if the tick is still bitten
Even if a tick bites someone - it does not mean that a person will get encephalitis. A person gets sick from ticks that are themselves infected with encephalitis. First of all, the tick must be pulled out. Keep in mind that the longer the tick sits, the harder it is to pull it out - another argument in favor of regular inspections.
Usually he digs into places where the tender skin, but it is the other way around. So be careful if the tick sucks in a non-classical place - where the skin is thick; in this case, he immediately "gnaws" very deeply and pull it much harder. The classical method of extraction is to grasp the tick with a thread loop and drop the Vaseline (saltolol, TSIATIM, any other fuel of medium density) so that the mite is completely closed.
After 5 minutes, start the periodic sipping of the thread - with due patience and without fanaticism. Gradually, the tick will be removed (it may take 15-20 minutes, be ready for this).
If the sucking individual has not yet had time to get drunk blood or is a tiny larva, then you can get rid of it with the help of a drop of vegetable oil, which you need to drop into the place of the bite, thus blocking the ticking of oxygen. Instead of butter, you can take cream, petroleum jelly or even kerosene. The insect itself, but only if it is alive, it is desirable to take it to the hospital for examination for the presence of infection. To do this, you need to put it in a jar with a wet fleece or several grass blades. The place of tick bite should be disinfected, and wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
Tick-borne encephalitis
A special danger for a person is a tick-borne encephalitis disease. It is for humans, because most animals tolerate this disease even without obvious clinical manifestations. According to statistics from 100 people who have treated with tick bites, about 10 are infected with this particular virus. Encephalitis is a terrible disease, leading to the defeat of the central nervous system and the motor center of a person, which can lead to paralysis, and the outcome is a long-term disability or even death. Consolatory is the fact that even in places of increased accumulation of ticks, no more than 5% of individuals are infected. Tick-borne encephalitis can not manifest itself even up to 25 days, on average the incubation period lasts from one to two weeks. Tick-borne encephalitis is manifested by the following symptoms:
High temperature (up to 40 °);
nausea and vomiting;
acute headache;
pain in the joints, muscles and throat;
diarrhea;
sweating;
general weakness.
In general, the disease manifests itself immediately in an acute form, but sometimes the period of exacerbation is preceded by a state of general weakness and malaise. In any case, if after a tick bite you become disturbed by the above symptoms, then immediately consult a doctor, as self-medication can be deadly.
The disease can go completely without consequences, but pareses, paralysis, muscle atrophy, as well as a significant decrease in the intellect and even the development of epilepsy are possible.
Precautionary measures
1. If possible, avoid the bush and do not allow children to climb in them.
2. Beware of arid areas and dead wood, do not walk in dense grass.
3. Remember that mites prefer deciduous forests. Therefore, a walk in the coniferous forest will be safer.
4. It is better to settle on water in sand, which is practically deadly for ticks.
5. For a long stay in nature, short sleeve t-shirts and shorts will not do. Your clothes should cover as much as possible all areas of the body. Ideal option is the presence of cuffs on the sleeves and elastics on the legs.
6. Going to nature, you need to think about your outfit so that there are as few open areas of the body as possible. Required and the presence of a headdress. Even when walking in the park, do not neglect it.
7. After you have returned from a walk, you should carefully examine all the outer clothing and shake it. Also, you should examine the body, and hair must be combed with a small comb.
8. It is desirable to camp with an overnight stay in tents to postpone until the hottest months, when ticks are less active. But in any case, the vegetation around the tent, as well as under it, is best burned out.
9. Coming from the woods, be sure to inspect your body and clothes, as well as pets that walked with you about the lurking bloodsuckers.
Folk remedies
As folk remedies against mites, tar, garlic and some essential oils are used.
Tar and essential oils, in particular tea tree oil, are used externally, that is, they rub open areas of the body. And garlic - internally, it is usually eaten before going.
Mixture to protect against ticks: 10 drops of essential oil of tea tree 50 ml of water (or cologne type "Chypre") Preparation: Mix the water and essential oil and pour the mixture into a vial. Shake before use. Apply a few drops of the mixture on the palm and rub them on the neck, hands, feet and hair. After returning from the forest, treat with a solution (using a spray) clothing.
Oil against mites for the shower.
15 drops of essential oil of tea tree 30 ml of detergent for shower. 5ml of soybean oil. Preparation: Mix the vegetable oil and the washing oil in a suitable container. Add the essential oil and mix again thoroughly. After a walk in the forest, take a shower with this oil. If the mite has already penetrated the skin, anoint his abdomen and skin around 100% with tea tree oil.
There is still a folk way, how to protect themselves from ticks: they chew pine needles, and swallow saliva. But this must be done slowly, and gradually. Since the spring. The tick to such people does not cling - crawls-crawls, secretions on the skin of sweat glands sniffs and sniffs, they do not like it, and will not bite a person with such a smell.
Borreliosis is a bacterial ailment. Its causative agent is the bacterium Borrelia.
This disease was discovered in 1975 by American infectious disease specialists.
In a small town of Lima in Connecticut, an epidemic of acute rheumatoid arthritis in children and adults, which had previously been bitten by a tick, erupted.
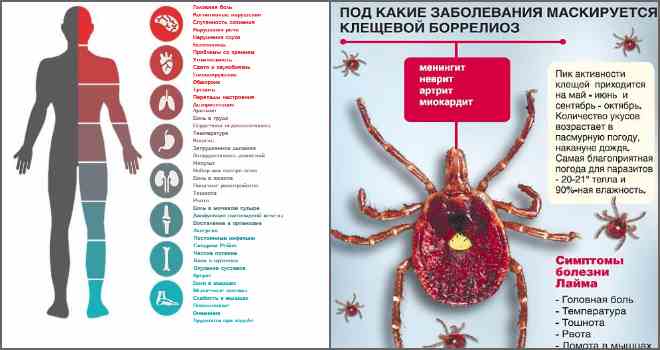
Lyme disease is the name for the American city in which the borreliosis epidemic arose
Scientists have identified the main sign of borreliosis - migratory ring-shaped erythema. The red spot has clear contours and sprawls across the skin at a decent distance from the lesion. Rings can be several, and they all have different thicknesses.
The skin at the site of the bite is inflamed and swollen.
If a person is transmitted from mites Lyme disease, the first symptoms are noted after 1 - 2 weeks. These include the following manifestations:
- increased body temperature;
- weakness in the muscles;
- chills;
- convulsions at night;
- general malaise;
- constant lethargy and drowsiness;
- the formation of a red ring around the place where the insect was;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pain in the bite.
If you do not consult a doctor, the condition continues to worsen. There are symptoms of meningoencephalitis or meningitis. A person is disturbed by severe migraines and insomnia. In addition, there is a significant memory impairment. The mental state raises fears. The mood changes frequently, flashes of anger appear, a person periodically falls into apathy and depression.
The tone of the occipital muscles rises, so it is impossible to move the neck. There is photophobia and abundant separation of tears.
A month later, in the absence of therapy, bacteria penetrate into all organs. Dangerous is the defeat of the trigeminal nerve. In this case, the functioning of the facial muscles is impaired. There is temporary or permanent paralysis. Postponed borreliosis affects the work of the heart and blood vessels. Later it threatens with chronic tachycardia, arrhythmia, shortness of breath, pain in the sternum, violation of oxygen metabolism in the blood, etc. 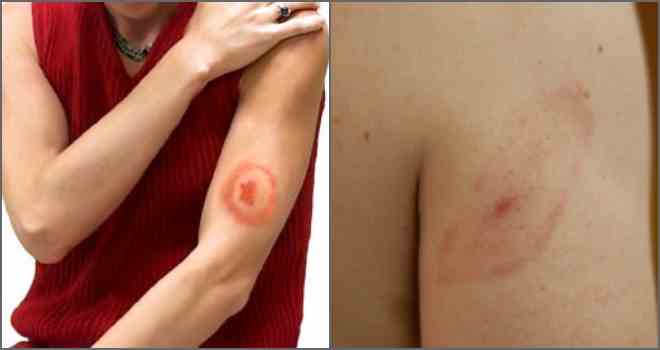
In childhood, Lyme disease is especially dangerous. If it is not cured in time, the baby can develop various diseases of the central nervous system, paresis and paralysis. With the consequences of borreliosis, it's hard to fight, so after a tick bite, you should immediately find out if infection has occurred or not.
Ehrlichiosis: manifestations of ailment
The incubation period with erlichiosis varies from 1 week to 20 days.
Later, the disease goes into an active stage, and the person manifests the first symptoms:
- increased body temperature;
- the formation of an ulcer or suppuration at the site of suction of an insect;
- redness of the affected area;
- soreness of the skin;
- strong intoxication of the body;
- nausea and periodic vomiting;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- permanent migraines;
- weakness.
The above mentioned signs are noted, as a rule, in children. Adult people suffer erlichiosis is not so difficult.
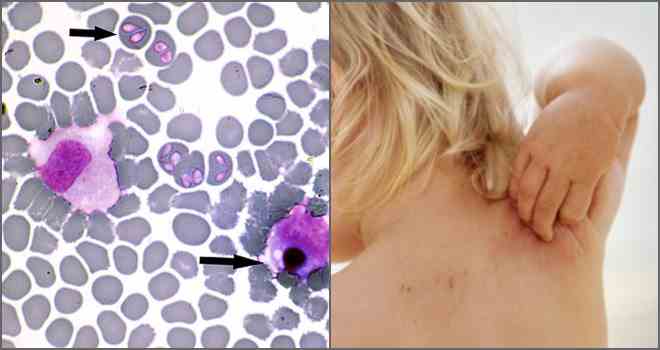
After 20 days after infection, signs of eruptions start to appear
In some cases, the symptoms are completely absent, and the person does not even know that he has had an erlichiosis. But this does not protect against the consequences of this disease, which include such violations:
- pathological changes in the spleen;
- expansion of the vessels of the face;
- enlargement of the liver;
- problems with metabolism;
- insufficient purification of blood from toxins and toxins.
In rare cases, with erlichiosis, a small rash is diagnosed throughout the body. D
this ailment is difficult to identify independently, therefore, it is recommended to carry the mite to medical examination for preventive purposes.
Relapsing fever
Recurrent typhus is one of the most dangerous diseases that can lead to sudden death.
The pathogen causative agent is Obermeyer's spirochete.
The primary carriers of this disease are rodents. From rats and mice, mites are infected with spirochetes, and later transferred to humans through blood. Recurrent typhus does not require specific treatment. A person is saved by his own immunity and antibodies, which are produced in the blood during the active stage of the disease.
Symptoms of recurrent tick-borne typhus are found a few days after the bite:
- formation of a dark papule in the affected area;
- spread of the rash all over the body;
- increase in body temperature up to 40 ° C;
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting;
- dizziness;
- fainting;
- pain in the muscles;
- an aching in the bones and twisting of the joints;
- severe dehydration of the skin;
- arrhythmia;
- tachycardia;
- disorders of the nervous system.
The acute stage passes when the body has developed enough antibodies to kill all the spirochetes. It is recommended to be under constant medical supervision. Differences in temperature and stress on the immune system can cause sudden death of a person.
If the doctor is nearby, the patient will be able to save in time, saving life.
Recurrent typhus is carried by argas mites, whose diseases are very dangerous for humans. Consequences of such ailment can be pneumonia, heart failure, liver problems and dysfunction of the central nervous system. To minimize the negative impact of recurrent typhus, you need to contact an infectious disease specialist. The doctor will prescribe the necessary prevention of all possible consequences.
Encephalitis: how dangerous and how manifested?
Even if you contact a doctor in a timely manner and get vaccinated, this will not save the victim from the negative effects of the disease.
Encephalitis affects the central nervous system. The head, back, brain and their shells cease to function properly. A person can partially or completely paralyze, speech and thinking processes are broken.
The encephalitis transmitted to a person from an insect is characterized by the following symptoms:
- weakness in the muscles;
- pain in the joints and bones;
- intoxication;
- migraines;
- periodic or permanent hearing impairment;
- lethargy and drowsiness;
- fast fatigue;
- an increase in body temperature to 41 ° C;
- numbness of the cervical musculature.
The first manifestations of the disease are observed on day 10.
This ailment does not pass by itself. Over time, the symptoms become more severe. There is paralysis, convulsions, mucous membranes acquire a bright red shade. The person needs to be urgently hospitalized.
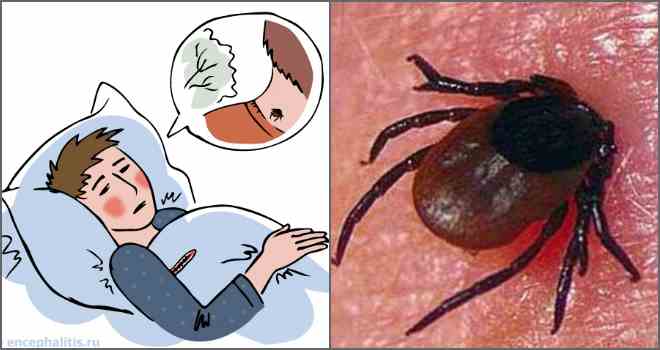
If suspected of tick-borne encephalitis, immediately hospitalize a person
Tick-borne encephalitis must be treated in a hospital.
In the hospital, the patient is washed with blood with the help of droppers, makes vaccinations and injects special preparations that neutralize the virus.
Tethered viral pathologies lead to a deep coma, and later - to death. When the first anxiety symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, and do not wait until the illness passes by yourself.
Spotted fever
Spotted fever is a serious bacterial disease. Bacteria penetrate into the nuclei of healthy cells and cause pathological changes in them. The organism reacts to similar processes by an acute allergic reaction.
Spotted fever develops rapidly and progresses rapidly. This ailment rarely leads to death. Recovering occurs when the active stage passes. In the body, immunity to the causative agent of the disease - the bacteria of the rickettsia group is developed. On the 2nd day after the insect bite, the first clinical symptoms begin to appear:
- bleeding from the nose;
- migraine;
- nausea and vomiting;
- loss of consciousness;
- increase in body temperature to 41 ° C at night;
- weakness;
- pain in bones and joints;
- night convulsions;
- temporary numbness of limbs;
- sleep disturbance.
Four days after the appearance of the first signs on the skin, numerous rashes of red are found. Nodules can merge, forming huge hyperpigmented areas on the surface of the epidermis.
In children, such formations cause itching and burning.
Babesiosis: Symptoms and Signs
The diseases that the mites suffer include babesiosis. This disease affects red blood cells - red blood cells.
The causative agents of pathology are the simplest microorganisms from the family Babesiidae.
Disease cells penetrate into the structure of the erythrocyte and gradually destroy it. A healthy person with normal immunity does not show babesiosis. In the blood instantly produced antibodies for the destruction of the simplest family Babesiidae.
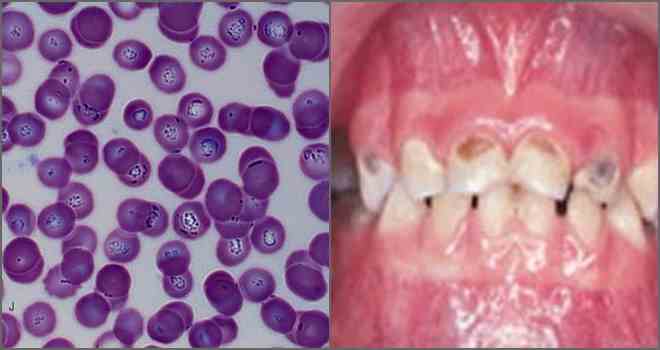
Babesiosis affects blood cells
Babesiosis occurs in an acute form in people with HIV or oncological pathologies. The disease manifests itself in those who have recently undergone transplantation of organs, recovered from infectious diseases or is infected with hepatitis. When immunity is weakened, then the following symptoms of babesiosis are noted:
- mucous membranes of yellow color;
- indigestion disorder;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness;
- headache;
- tachycardia;
- dyspnea;
- urine of dark shade;
- constipation;
- intoxication.
If you do not seek medical treatment for a long time, oxygen starvation begins.
The number of red blood cells decreases, and the lungs do not get enough air.
Because of this, kidney, heart and liver failure develop. People with low immunity can die from babesiosis, if not on time to undergo a therapeutic course.
Tularemia: the distinctive features of the disease
The infections transmitted by mites can have serious consequences, and tularemia is no exception. The pathogen of this pathology is a bacterium of the genus Francisella tularensis.
Symptoms of the disease depend on which area of the body was affected.
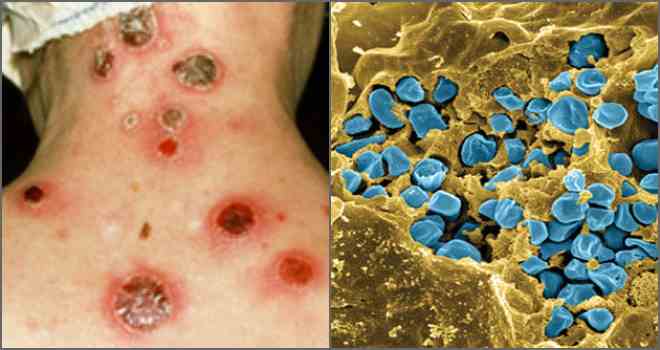
Skin lesions with tularemia
7 days after infection, the first signs of the disease appear:
- redness of mucous membranes;
- change in skin color at the site of injury;
- the growth of crusts in the area of an insect bite;
- headache;
- weakness;
- increase in temperature to 41 ° C;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- accumulation of pus in the lymph nodes;
- muscle pain.
The active stage of tularemia is the heaviest for a person. When the first symptoms appear, you need to urgently go to the hospital.
During an acute period, the lymph nodes become inflamed and filled with pus.
Later they are opened, and the contents flow out of them. It is extremely important that this process takes place under the supervision of a doctor. Otherwise, fistulas and other dangerous complications of tularemia can be formed.
With the onset of spring heat, pleasant walks in the park or forest planting can be overshadowed by the bite of a tick, not only the person himself, but also the pet walking with him. To protect themselves and animals from tick-borne attacks, it is better to have an idea of where the ticks live and how they multiply.
What are ticks?
Mites are just small arachnid arthropods that have lived for millions of years and inhabited the Earth long before the appearance of a human being on it. Therefore, it can be argued that how much a person lives, so much is accompanied by the bites of representatives of this family.
Mites can be rightly attributed to the faithful and constant companions of all living things - for millions of years, where there is vegetation or living creatures, you can meet these spiders from hot Africa to the harsh taiga of the Eurasian continent, from deserts to moist forests. That is, it is difficult to find a place on the planet where mites do not live.
The remaining mites inhabit various vegetation, feed on plant components, organic matter, their relatives or their remains, without presenting any threat to humans.
Which mites are dangerous to humans and pets
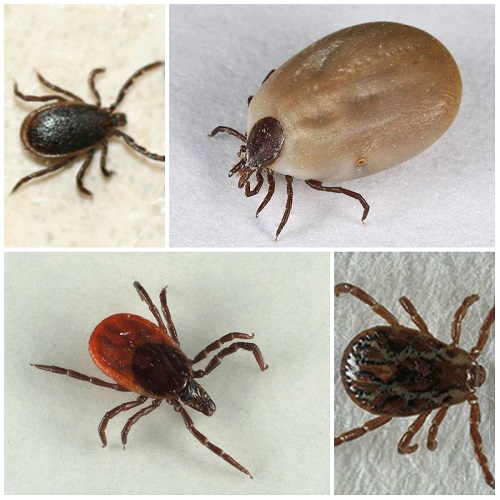

- ear mites, affecting the external ear and auditory passage;
- itchy itching, affecting the subcutaneous layers;
- demodicosis, when the person and the area around him are mostly affected.
Prevention is the strict implementation of hygiene rules, especially where such ticks and their carriers live.

Argas and ixodid mites
It is their random bites, possible during walks and trips to nature, people rightly fear, wanting to avoid the following unpleasant and sometimes dangerous moments:
- infection bitten by pathogens of serious diseases;
- itching and allergic reactions;
- dermatitis and other skin lesions.
Argassic tongs

Not all representatives of argasid mites are able in our band to harm their attacks, mostly from their majority sufferers in South America.

Where do the ticks live and how do they end up on the victim?
As soon as the earth's cover warms up over 5 degrees, bloodsuckers crawl out of the last year's grass to their patient hunt, waiting for a likely suitable victim from the representatives of warm-blooded animals to pass by.
They do not live on trees, preferring the grassy wet cover, as they think. Having climbed a blade of grass, a branch of a bush, a knot, bloodsuckers can do as much as they like, sometimes for months, wait for the source of food, to cling to their wool or clothes with the claws on their paws, and reach the skin with a help of special suckers to gain a foothold on it and carry out a bite.

As much as a tick can climb, climbing up depends on the stage of maturation - the larva is a nymph or an adult spider.
- The larva of an ixodid mite above 30 cm is not able to climb, so it feeds on the blood of small animals and birds. One "feast" is enough, which can last for several days, and the larva falls into the grass to continue the transformation. For humans it is an unlikely threat of sucking.
- The nymph can already afford to climb higher to increase the chance to meet a potential warm-blooded victim. But she can rarely overcome more than a meter. Nymphs also have enough one-off saturation, and a person may well become her probable casual "breadwinner".
- An adult mite above a meter and a half is difficult to meet. This is the maximum height with which it can reach the body of its victim. It is adult bloodsuckers that actively attack people and animals, including large ones.
Therefore, it is wrong to avoid places where trees grow. In fact, you need to be wary of thickets of grass and shrubs, try not to walk at the edge of the path, do not choose to spend an overnight stay or picnic wild grass lawns. It is better to prefer "bald" glades, and in a pine forest on a dry layer of fallen pine needles, where there is no grass, it is completely unreal to meet a tick.
Than Ixodid mites are dangerous
The highest risk in a tick bite is the transmission of the encephalitis pathogen to the victim.
- When untimely treatment, a person is threatened with death. The statistics for Russia testifies about 2 300 cases of infection with tick-borne encephalitis in 2015, 24 people died. The only protective effective measure is vaccination against encephalitis.
- The second danger is the transmission at the sting of a bloodsucker of Lyme disease, or borreliosis, which, with inadequate or untimely prescribed treatment, leads to severe disability and even death.
- For pets, there is an increased risk of getting sick after a tick attack with pyroplasmosis, resulting in the animal dying if not started therapy immediately after the attack of the tick.
The carriers in the northern hemisphere of these diseases in most cases are 2 types of ixodid mites - taiga and canine.
How do I get rid of ticks?
- Sexually mature female, drinking a lot of blood, puts a huge number of eggs in the grass, more than 15 000. But how many of them will live up to the stage of imago, depends largely on environmental conditions. Usually several dozen spiders become so lucky. The process of maturation of masonry lasts several weeks.
- A hatched larva feeds on blood once. Since she is not accessible to heights, she is forced to attack small warm-blooded. "Feast" can last for several days, after which it falls into the grass and, digesting sucked blood, is transformed to the next stage of the nymph. This process is often stretched to fall, and the nymphs remain wintering at this stage.
- In the spring with the first heat, the nymph is ready to hunt. She is already able to climb larger animals. Once she has eaten once, she will ripen to an adult for about a year.
- The male of a mature mite sucks blood from half an hour to several hours, which is necessary for him to mate.
Ixodid mites in the bite of the skin inject an enzyme with an analgesic.
Measures to protect against tick-borne attacks
Going to the park, forest, landing, use a repellent of any shape, put on closed clothing, protect the pet with drops, spray or collar. Returning, carefully examine the body and, after finding the tick, remove it competently.
If you live in a dangerous zone, teeming with ticks, or plan a trip there, vaccination will be the best preventative measure.
About annoying people, we usually say: "I grabbed like a tick". This is quite an appropriate comparison, since getting rid of a tick is not at all easy. And it is important to remember that the tick is a vector of dangerous diseases, its bite can lead to paralysis, deafness and even death.
Infected with a tick or not, it is impossible to determine by itself. How can you protect yourself from a tick bite?
The enemy must be known "in person".
There are more than 60 thousand species of ticks: from the smallest size of 0.08 mm and to the largest - 3 cm in length. Males are smaller than females, and they suck on the skin of a person for a short time - not more than an hour. The female can suck blood for many days and when it is fully saturated, then its weight increases in 80-120 times. Ticks do not have eyes, but they have a well-developed sense of touch and smell, which helps them catch the smell of the victim from a distance of 10 meters.
When are ticks most dangerous to humans?
In the beginning or middle of April, when the sun is warming, the activity of mites begins to manifest. Their numbers are gradually increasing and reaching a peak by the second decade of May. And, depending on the weather, the high risk of tick bite lasts until the end of June. Then the danger decreases, but individual individuals can be active by the end of September.
Where can I find ticks?
Ticks love wet places, so they are mostly in moderately shaded forests, where there is a thick grass and undergrowth. But they also occur in forest fringes, in willow beds, in ravines, on paths overgrown with grass, along the banks of streams.
How do mites get on a person?
Many are mistaken, believing that the mites jumped on the person from the trees. In fact, they cling to clothes from below, with small shrubs or high dry grass, and then crawl up. Therefore, a false idea is created that he fell from above. When the tick senses the smell of blood, it quickly jumps on its prey, spreading the front legs with special claws and suction cups, fixed with their help on clothes, and then makes its way to the power source.
Most often ticks suck on the scalp, on the ears, in the neck and clavicles, underarms, on the chest and back, in the inguinal zone, and in children can even on the eyelids.
Infection with mites.
The sucking mite secretes saliva in the wound. The first saliva, like glue, firmly adheres its proboscis to the skin of a person. Saliva, which is released later, performs several functions: anaesthetizes the wound, destroys surrounding tissues and walls of blood vessels, suppresses the immune system of its prey and spreads the infection by blood.
Currently, the medicine identifies five types of infections. The most common of these are tick-borne encephalitis and tick-borne borelliosis.
Protection against ticks.
If you live in a zone of increased danger of ticks, you need to get vaccinated in advance, which in case of a bite will relieve the unpleasant consequences.
Going to nature, get a special repellent repelling mites, and treat them with clothes. Apply it to the collar and cuffs, to the waist and to the top of the socks - then the mites do not penetrate under the clothes.
Clothing is better to choose light colors, tight body. The shirt is tucked into the trousers, and the trousers are tucked into the boots. On the head and neck tie a handkerchief.
Every 1.5-2 hours of outdoor recreation, do a self-test and inspect each other. Arriving home, too, carefully examine all clothing and body.
Do not neglect these precautionary measures so that with the onset of heat you do not have to go to a medical institution with a tick bite.
How to pull a tick?
Remove the sucking mite carefully so that its head does not remain in the human body. Grab the tick with tweezers or wrapped cloth with your fingers, do slow, smooth movements.
If this method fails to remove the tick, lubricate it with vegetable oil or petroleum jelly and after 10-15 minutes again try to pull it out. There are times when the mite crawls out by itself.
The place of the bite must be treated - it will suit alcohol, iodine, cologne or zelenka.
Wash hands thoroughly with soap after all procedures.
Tick must be checked for infection with encephalitis virus.
Within a month after the bite, you need to closely monitor the wound and overall well-being.
When to see a doctor after a tick bite?
If, while extracting the tick, his head came off and remained in the wound.
When swelling and redness of the bite.
When there are symptoms: high fever, headache, fever, difficult movements of the neck and eyes, photophobia.

